ASCII CODE AND EBCDIC CODE
Hello friends, today we learn about gray code and bcd code in it, so let's start
ASCII CODE AND EBCDIC CODE
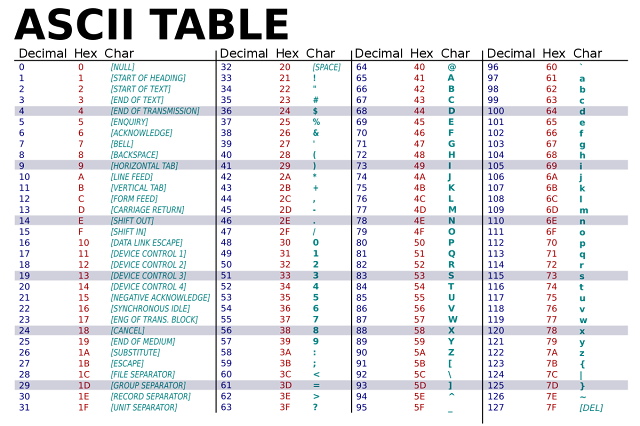
ASCII CODE-:
ASCII stands for “American
standard code for information interchanges “, It has become a world standard
alphanumeric code for micro-computer. It is a 7-bit code and it can represent
maximum 27=128 different characters. These character represent 26
uppercase letter (A-Z), 26 lowercase letter (a-z), 10 digit(0-9), 33 special
symbol character and 33 control characters.
The 7 bit
of this code are divided into two parts. First 3 bit of left are called zone
bits and next four bits of right side are called numeric bits.
 |
| ASCII CODE AND EBCDIC CODE |
An 8 bits version of ASCII code is also available , which is know as USACC-II or ASCII-8. They can represent maximum of 256 characters.
- Learn Gray code and BCD code, click here
- Learn characteristic and limitation of computer, click here
- Learn what is hardware and software,click here
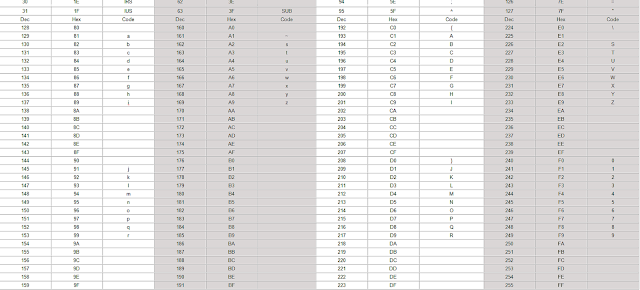
EBCDIC code-:
EBCDIC stands for “Extended binary
coded decimal interchanges”. It is basically used for large computer like a mainframe. It ia an 8-bit code and with the help of this code we can represent
maximum 28=256 characters. The 8 bit of EBCDIC code is know as zone bits and
last four bits are known as numeric bits.
EBCDIC Table -:
 |
| ASCII CODE AND EBCDIC CODE |
 |
| ASCII CODE AND EBCDIC CODE |
Note: Values are based on the 0-255 scale.
Example -: ASCII to EBCDIC Conversion, COBOL functions require a 1-256 scale;
Note: Values are based on the 0-255 scale.
Example -: ASCII to EBCDIC Conversion, COBOL functions require a 1-256 scale;
ASCII or EBCDIC character is
represent by 2 hexadecimal digit. For example, ASCII character E is hexadecimal
45 or X'45'. To find the location of the ASCII character E , you can go down to
row 4. Second hexadecimal digit is 5,
you can move across to column 5. point at which they meet the hexadecimal value X'C5'. This hexadecimal
EBCDIC value for E is X'C5'. If you want the E to be represented by a different
EBCDIC hexadecimal value you can edit this value in this table. When a transfer
has completed and the data is converted to EBCDIC, the new value is used.
- Learn Gray code and BCD code, click here
- Learn characteristic and limitation of computer, click here
- Learn what is hardware and software,click here


Comments
Post a Comment